The document outlines criteria for symbols utilized in labeling medical devices to communicate information regarding their safe and efficient usage. It additionally enumerates symbols that meet these criteria. This guideline pertains to symbols employed across various medical devices sold worldwide, necessitating compliance with diverse regulatory standards. These symbols may feature on the medical device, its packaging, or accompanying documentation. However, it’s important to note that this document’s specifications do not extend to symbols outlined in alternate standards.
What are the FDA requirements for medical device labeling?
The FDA’s medical device labeling requirements, outlined in 21 CFR Part 801, ensure labels provide accurate, clear, and sufficient information. Key requirements include:
1. General Labeling: Labels must display the device name, intended use, and the manufacturer’s name and address. They should include adequate directions for use, warnings, precautions, and contraindications.
2. Unique Device Identification (UDI): Most devices must have a UDI in both human- and machine-readable formats, submitted to the FDA’s GUDID database.
3. Specific Device Requirements: Certain devices (e.g., hearing aids, in vitro diagnostics) must follow additional labeling rules under Subpart H or 21 CFR Part 809.
4. Language: Labels must be in English unless distributed in territories where another language is dominant.
5. Sterility and Expiration: Sterile devices must indicate sterility, sterilization methods, and expiration dates.
6. Professional vs. Lay Use: Labels for laypersons must use simple language, while professional-use devices require technical details.
Noncompliance can result in misbranding, penalties, recalls, or import/export restrictions. These requirements aim to ensure safe and effective device use.
Suggested Read:
Unique Device Identification (UDI) Requirements in EU MDR
Background of ISO 15223
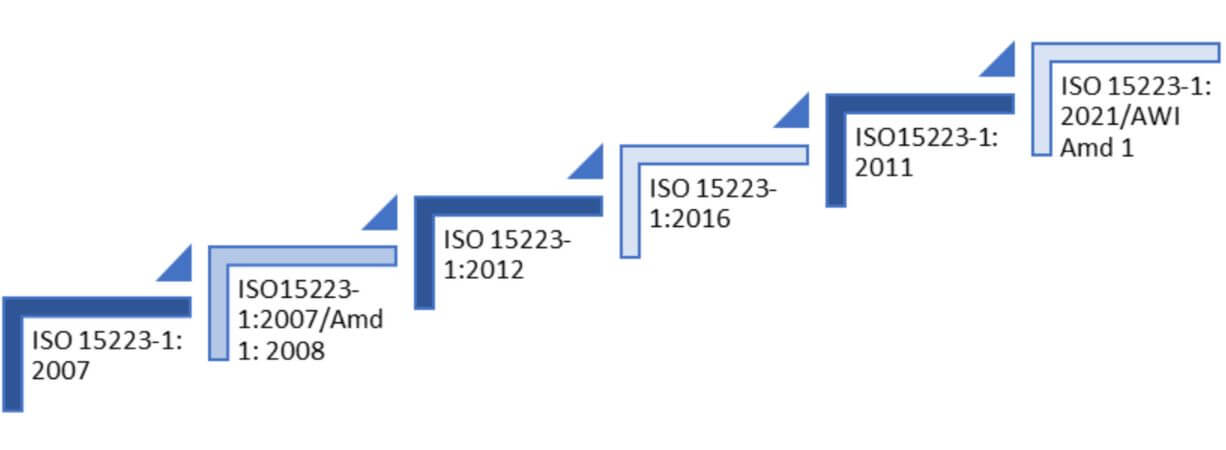
The history behind ISO 15223 is extensive, having developed through collaboration among industry specialists and stakeholders. Its publication aimed to establish a universally comprehensible set of symbols and labeling standards. ISO 15223 has achieved widespread recognition and implementation within the medical device industry on a global scale.
Global labeling standards for medical devices ensure safety and regulatory compliance across markets. Key regulatory bodies include:
Global Labeling Standards and Regulatory Bodies
1. United States (FDA): Governed by 21 CFR Part 801, focusing on clear labeling, UDI, sterility, and intended use.
2. European Union (EU MDR/IVDR): Requires CE marking, UDI, language translations, and compliance with Annex I, Chapter III for safety and performance.
3. Canada (Health Canada): Labels must meet SOR/98-282 with bilingual (English/French) requirements and UDI for Class II-IV devices.
4. Japan (PMDA): Labeling adheres to the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act, requiring Japanese translations and specific packaging rules.
5. China (NMPA): Labels must follow the Regulations for Medical Device Supervision and Administration, including unique device codes and Chinese translations.
6. Australia (TGA): Aligns with ISO 15223-1, requiring detailed labeling, UDI, and ARTG registration.
Global standards like ISO 15223-1 and ISO 20417 ensure consistency in symbols and information. Compliance varies by region, emphasizing localization.
Significance of Symbol
Symbols are visual representations found on the label or accompanying documents of a medical device. They convey important information without requiring the reader to understand a specific language of any nation or culture.
Suggested Read:
Importance of Clinical Data in EU MDR Compliance & Device Safety
Benefits and Impact
The adoption of ISO 15223 yields concrete advantages. Enhanced patient safety, simplified global commerce, and better communication between stakeholders are among the notable outcomes. We’ll explore case studies and practical instances illustrating the significant influence of following this standard.
Amendments of guidelines
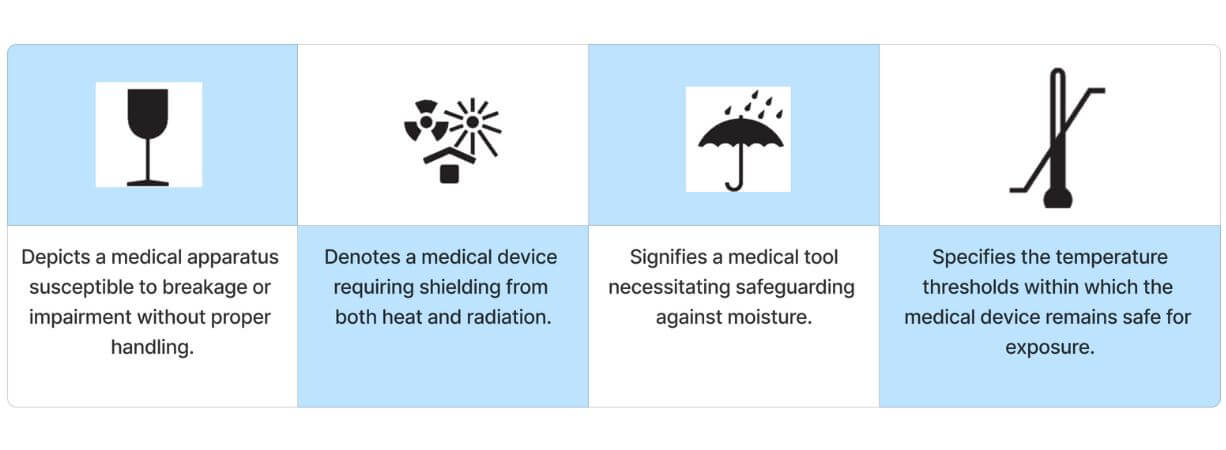
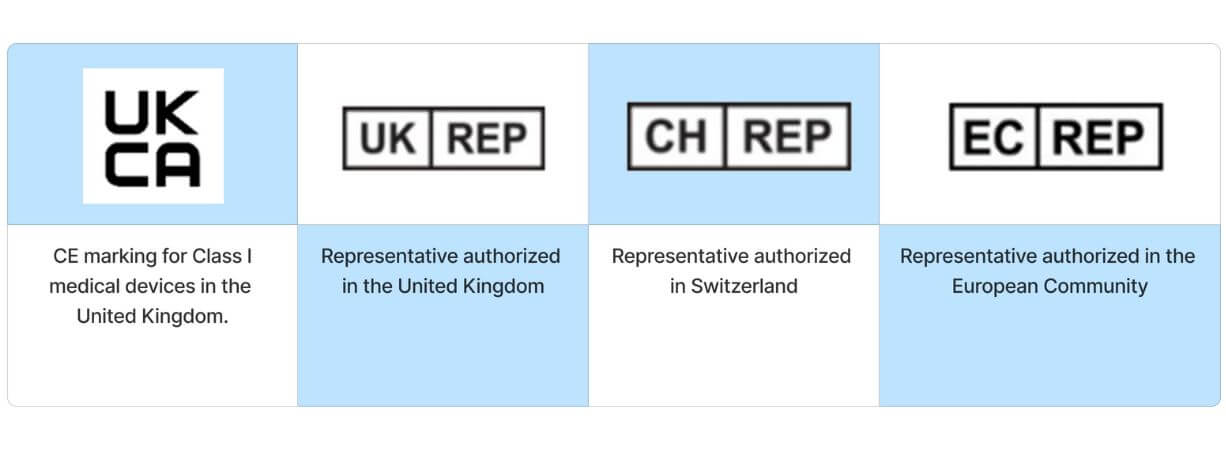
Commonly used symbols on medical device
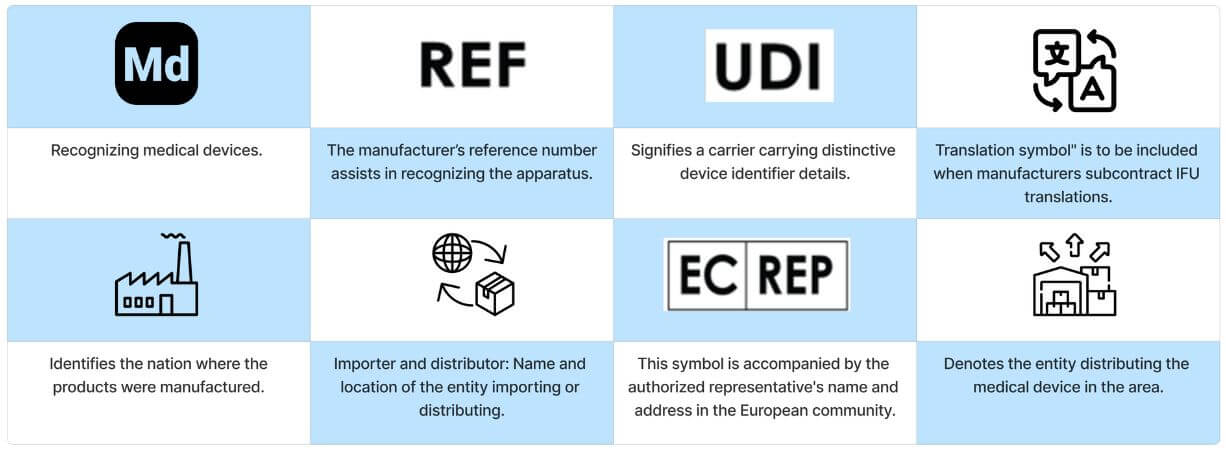
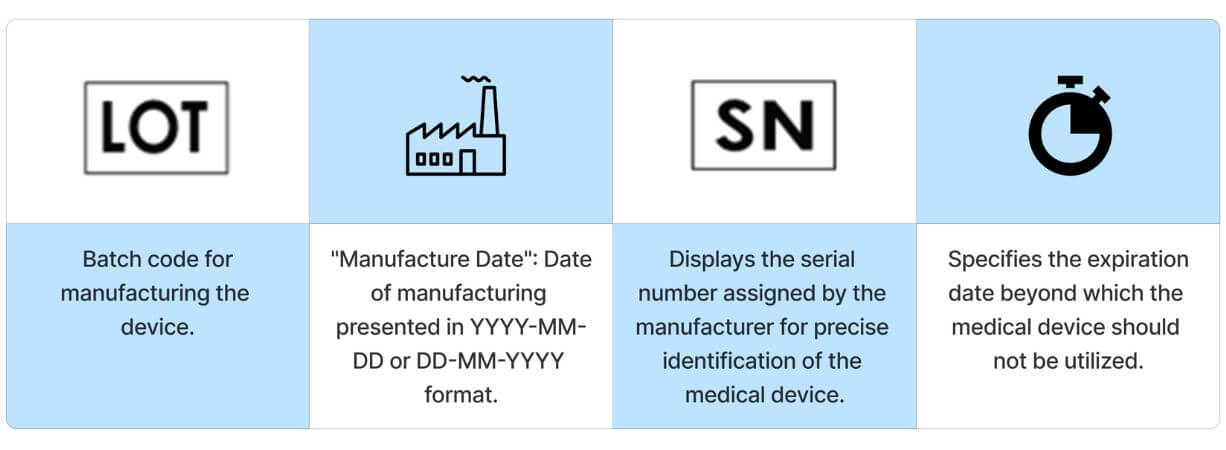
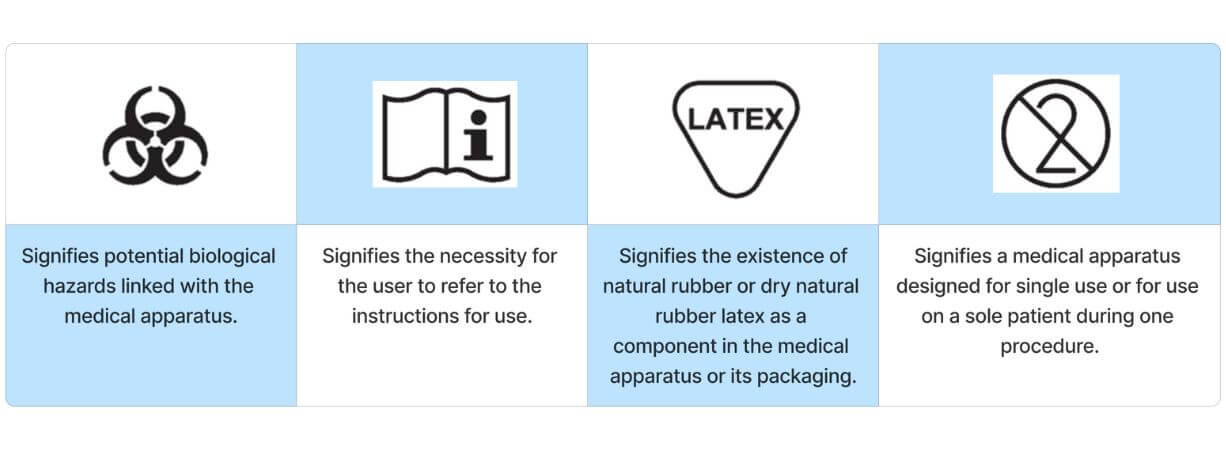
Frequently utilized symbols found on medical devices serve to provide users with general information about the device and to display its unique identification number.
General Symbols
Manufacturer Symbols
Sterile Symbols
Safety Symbol
Storage symbol
Country specific
Materials substances
Challenges in Multi-Country Medical Device Labeling
Multi-country medical device labeling faces several challenges due to varying regulatory, linguistic, and cultural requirements:
1. Regulatory Variations: Different countries have unique standards (e.g., FDA in the U.S., EU MDR in Europe, NMPA in China). Ensuring compliance with diverse regulations, including UDI requirements, language, and format, is complex.
2. Language and Translation: Labels must be translated into local languages, often requiring multiple versions for countries like Canada (English/French) or the EU (over 24 languages). Poor translations can lead to misinterpretation and safety risks.
3. Symbol Standardization: While ISO 15223-1 standardizes symbols, not all countries adopt the same guidelines, leading to inconsistencies.
4. Cultural Differences: Graphics, colors, and symbols may carry different meanings across cultures, necessitating localization to avoid misunderstandings.
5. Frequent Regulatory Updates: Regions often update labeling requirements, such as the EU MDR or China’s NMPA rules, requiring constant monitoring and updates.
6. Packaging Constraints: Limited label space makes it difficult to include all required information in multiple languages and formats.
7. Cost and Time: Designing and producing compliant labels for multiple markets can be resource-intensive.
Addressing these challenges requires robust regulatory knowledge, careful planning, and streamlined processes to ensure global compliance.
Maven Profcon Services: Streamlining Global Medical Device Labeling for Safety
Maven Profcon Services streamlines global medical device labeling by ensuring compliance with international regulations, including FDA, EU MDR, etc. We offer end-to-end solutions, including UDI implementation, multilingual translations, and symbol standardization, tailored to meet the unique requirements of each market. Our expertise in regulatory updates, cultural localization, and efficient label design enhances safety and clarity while minimizing risks. By simplifying complex global labeling processes, Maven Profcon helps manufacturers achieve compliance, improve operational efficiency, and accelerate time-to-market for their medical devices.
References
International standard ISO – 15223 -1:2021
Glossary of standard symbols.