Introduction to Strategic Sampling
Quality control is a critical aspect of any organization’s operations, ensuring products meet specified standards and customer expectations. ISO 2859-1:1999(E) plays a pivotal role by providing a structured approach to sampling inspection. ISO 2859-1:1999(E) elucidates the importance of acceptance quality limit (AQL).
Key Concepts in Sampling
Acceptance Quality Limit ( AQL)
The Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL) is a statistical measurement used for the sampling plans and schemes provided in the ISO 2859 standard. It indicates the maximum acceptable number of defective goods in a particular sample size. A specific value of the AQL is designated for a certain nonconformity or nonconformities, it indicates that the sampling scheme will accept the majority of the lots. The AQL is a parameter of the sampling plan. Different AQLs may be designated for different groups of nonconformities. The AQL values shall not exceed 10% of nonconforming products when the quality level is expressed as a percentage of non-conforming products.
Time for Drawing samples
The process of drawing samples from a lot can be done using simple random sampling or stratified sampling. In simple random sampling, the items are selected from the lot in a random and unbiased manner. On the other hand, when the lot consists of sub-lots or groups, identified by some rational criterion, stratified sampling is used. This involves breaking the population of interest into groups and selecting samples from each group in a way that the size of the subsample from each group is proportional to the size of that population. This ensures that the sample is representative of the entire lot, especially when there are different characteristics within the lot. The samples can be drawn after the lot has been produced or during production, and when double or multiple sampling is used, each subsequent sample is selected from the same lot.
Sampling Plans
The most important element of accepting sampling is choosing an appropriate sampling plan, which specifies the lot size, sampling size, number of samples, and the acceptance/rejection criteria.
Considering all these parameters, acceptance sampling is of three types:
- Single Sampling Plan: The sample size specified in the plan determines the number of items inspected. If the count of defective items found in the sample meets or falls below the acceptance level, the lot is considered acceptable. Conversely, if the count exceeds the rejection threshold, the lot is considered unacceptable.
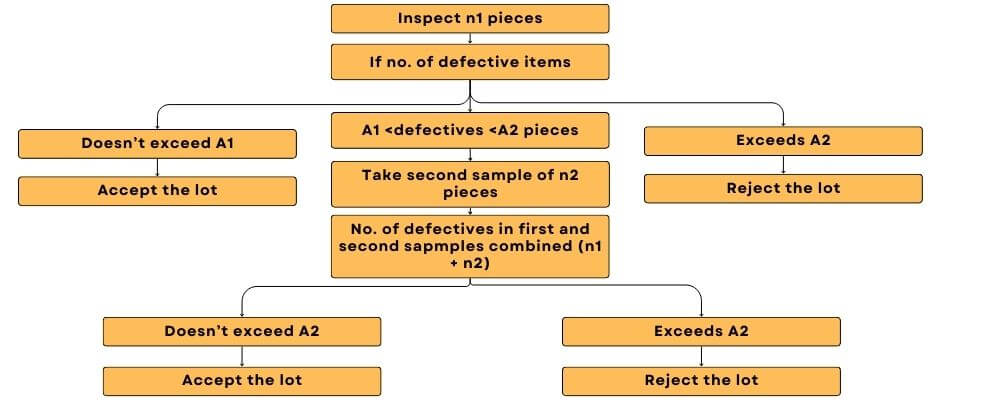
- Double sampling plan: The sample size specified in the plan is inspected. If the number of defective items found is within the first acceptance threshold, the lot passes. However, if it exceeds the first rejection threshold, the lot fails. If defects fall in between, a second sample of the same size is inspected. The cumulative defects from both samples determine acceptance or rejection based on the second acceptance and rejection thresholds.
Let N = lot size, n1 = number of pieces in the first sample, A1 = acceptance number for first sample, n2 = number of pieces in the second sample, n1 + n2 = number of pieces in two samples combined, A2 = acceptance number for the two samples combined.
- Multiple sampling plan: If the inspection process involves more than two samples, the decision to accept or reject the lot is made based on the cumulative number of defective items. If this total exceeds the upper limit specified for a sample, the lot is rejected. Conversely, if the total is equal to or less than the lower limit the lot is accepted.
Inspection Level
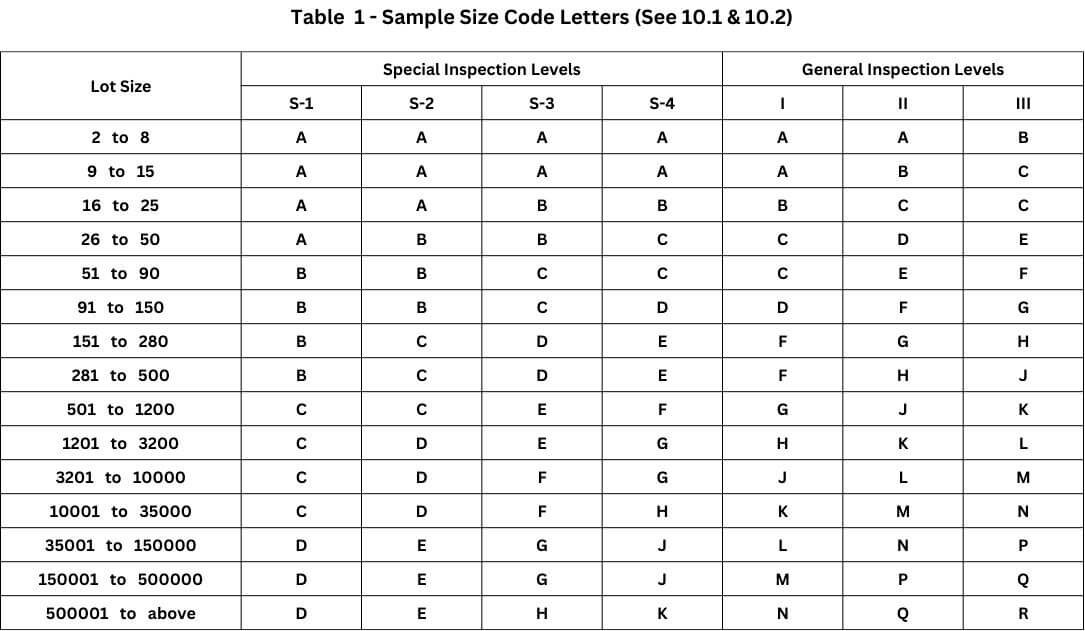
The inspection level designates the amount of inspection to be carried out. There are three general inspection levels (I, II, and III) and four additional special levels (S-1, S-2, S-3, and S-4) provided in the standard. The responsible authority specifies the inspection level for a particular application, allowing for greater or lesser discrimination as needed.
Lot Inspection using ISO 2859-1:1999(E)
Let us consider that we have received 1,000 batteries from a supplier and we want to determine a sampling plan for inspection. In that case what will be the sample size and criteria for acceptance if AQL is 1% for General Inspection Level II?
Table 1 corresponds to, the sample size code letter, i.e., General Inspection Level II and Lot Size range of 501 to 1,200 ( lot size 1,000 as stated above) is “J.” Now, in Table 2, refer to sample size code letter “J,” we will get the prescribed number of samples, which is 80. From the same Table 2, for AQL of 1% and sample size as 80, we will get the Acceptance number (Ac) = 2, and the Rejection number (Re) = 3. This implies that if two or fewer defects are found in the sample, accept the lot. Similarly, if the number of defects is three or more, then reject the lot.
Also Explore:
Medical Device Quality Management System Overview
Challenges in Strategic Sampling
1. Defining a Representative Sample: Ensuring the sample accurately represents the broader population is challenging, especially in heterogeneous groups, leading to potential bias.
2. Resource Constraints: Limited time, budget, or access to participants can reduce the effectiveness and scope of sampling efforts.
3. Sample Size Adequacy: Determining the right sample size is crucial for statistical validity; too small a sample can lead to unreliable results, while too large can be inefficient.
4. Ethical Concerns:Handling sensitive groups and ensuring fairness, confidentiality, and informed consent can complicate sampling processes.
5. External Factors: Geographic, cultural, or logistical issues may affect participant availability and data collection efficiency.
Maven Profcon Services: Optimizing Data Collection with Strategic Sampling
Maven Profcon Services specializes in optimizing data collection through strategic sampling techniques to ensure accurate, representative, and unbiased results. We understand the challenges of defining the right sample, particularly in diverse populations, and work to address potential biases while maintaining ethical standards. By leveraging advanced methodologies and technologies, we streamline the sampling process, ensuring that sample size is adequate for reliable statistical analysis. Our approach helps organizations gather high-quality data while adhering to regulatory requirements, ultimately driving better decision-making, improved outcomes, and enhanced research capabilities in healthcare industries.