The risk management standard ISO 14971:2019 is the Holy Bible for medical device risk management. As elegant as it has been presented on its own, one could consider it as ISO’s tip of the hat to acknowledge Regulation (EU) 2017/745, the EU MDR. As a successor to ISO 14971:2007, the updated standard has introduced crisp clarifications on previously defined concepts and even restructured certain requirements, aiming for a better fit. Furthermore, a separate guidance document, the ISO/TR 24971:2020 has been published to cater the application perspective of the ISO 14971:2019.
The estimation and evaluation of overall residual risk is one of such requirements where a detailed clarity is provided by the standard and its associated guidance document. It is now a requirement to document the method for the evaluation of the overall residual risk and the criteria for its acceptability in the risk management plan and policy. Not surprisingly, the criteria for acceptability of the individual risks may significantly differ from the criteria for acceptability of the overall residual risk.
The overall residual risk posed by a medical device can be imagined as an aggregation of the contributions of individual residual risks, i.e., the risk that is present even after the application of all possible control measures against each of the individual risks.
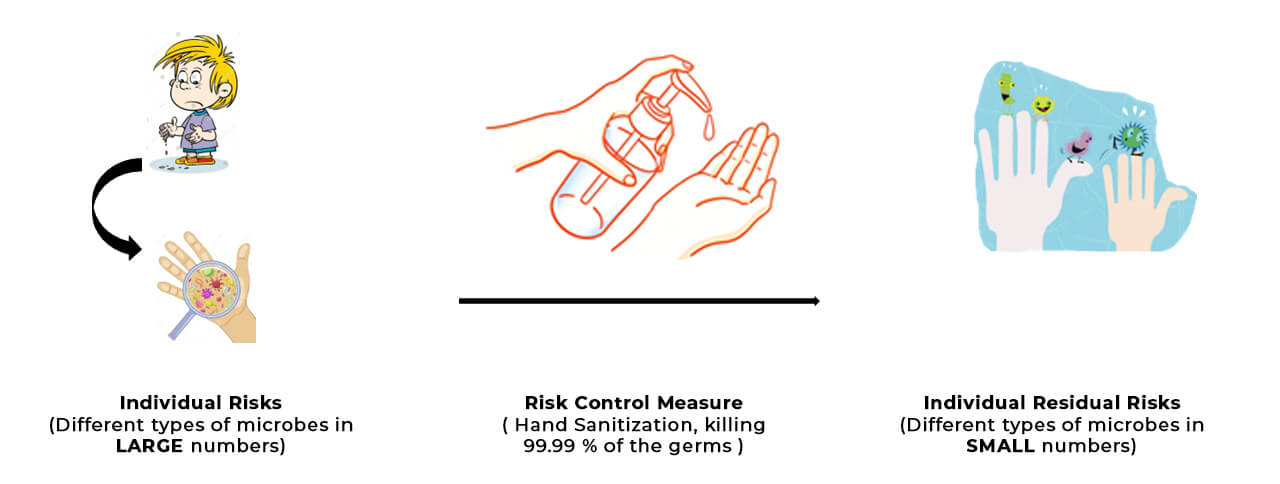
Let me paint the picture here… Imagine that you want to get your hands sanitized. Each type of germ (a bacteria/virus/fungi/etc.) in your hand represents an individual risk. On applying the sanitizer (risk control measure), you could possibly achieve 99.99% disinfection. The left-over types of germs in your hands, despite applying the best sanitizer available, represent the residual risks!
In this case, the overall residual risk can be visualized as the COLLECTION of all types of left-over germs that are present in your hand, as shown below. Now that’s quite a picture, isn’t it!?
It is very important to note here that the overall residual risk is NOT merely a sum or average of the risk ratings of all individual residual risks. For example, you cannot add a bacterium with a fungus, because they are different types of microbes causing different types of diseases. Each residual risk has an identity of its own, and the overall residual risk is only a representation of the DISTRIBUTION of all the residual individual risks.
“The evaluation of overall residual risk is the point where residual risk is viewed from a broad perspective.” – Pg 22, Section 8.1 General Considerations, ISO/TR 24971:2020.
“The evaluation of overall residual risk is a challenging task that cannot be achieved by adding all individual risks numerically.” – Pg 23, Section 8.1 General Considerations, ISO/TR 24971:2020.
Residual Risk: Analyzing One Approach from ISO/TR 24971:2020 (Section 8.3(b))
ISO/TR 24971:2020 offers 6 different approaches for the manufacturer to estimate and evaluate the overall residual risk of a medical device. We shall investigate one of these approaches in accordance with Section 8.3 (b) of ISO 24971:2020, that is to adopt the visual representation method, giving a graphic view of the distributions of the residual risks.
Imagine that a manufacturer identifies 50 risks in total for its medical device and gives each of the risk a score (risk rating/critical number) based on probability of its occurrence and its severity. This is how the distribution of the 50 risks would look like, before applying any control measures:
BEFORE APPLYING CONTROL MEASURES:
Do you see what the problem is here? There are clusters of risks which are found near the borderline region (The junction between yellow and red regions, i.e., the boundary of non-acceptability); There are a large number of risks in the non-acceptable region (red region) and too few risks in the acceptable region (green region). The linear trendline (in blue color) depicts that the highest distribution of all the residual risks is found in the non-acceptable region. Therefore, the overall residual risk is deemed NOT ACCEPTABLE. There is a requirement of control measures to be implemented.
Now, consider that suitable control measures are implemented by the manufacturer. Let us have a look at the distribution of all the residual risks now.
AFTER APPLYING CONTROL MEASURES:
There are no clusters of risks which are found near the borderline region (The junction between yellow and red regions, i.e., the boundary of non-acceptability); There are zero number of risks in the non-acceptable region (red region) and a large chunk of the residual risks lie in the acceptable region (green region). The linear trendline (in blue color) depicts that the highest distribution of all the residual risks is found in the acceptable region. Therefore, the overall residual risk is deemed ACCEPTABLE. There is no requirement of further control measures to be implemented.
That was very easy, wasn’t it!? There you go, that’s how you evaluate the overall residual risk and judge its acceptability!
It is important to note that the manufacturer needs to apply suitable control measures to reduce the risk to as far as possible levels to bring the residual risks closer to the green region. There are cases where, despite applying the best individual control measures, clusters of residual risks remain in the yellow region close to the borderline. In such situations, it is important that the manufacturer takes further corrective actions and re-investigate control measures to introduce possible design changes to ensure acceptability of the overall residual risk.
In other words, deeming every individual residual risk as acceptable by deploying a benefit-risk analysis may not be sufficient enough to deem the overall residual risk as acceptable. Moreover, if the overall residual risk is not judged acceptable, then the medical device cannot be declared as safe.
CONCLUSION
The estimation and evaluation of overall residual risk remains one of the most fascinating, yet challenging aspects to medical device manufacturers. Adopting a suitable measure to adequately perform an analysis of the overall residual risk posed by a medical device and thereby judging it acceptable/not-acceptable needs careful thought and rationale. The method depicted in this blog is a reasonable approach to implement the same, and we at Maven offers you a custom-made residual risk graph generator, in case you wish to evaluate the residual risks of your medical device at ease!