What is a clean room?
Hi there! You know how certain industries have these specific rooms, particularly for manufacturing Healthcare products? Those are clean rooms, though. Consider these the VIP sections of the manufacturing process.
To put it simply, a clean room is an extremely regulated area created to exclude even the smallest particles, such as dust and microorganisms. The goal is to establish a space where the air is extremely filtered and there is little possibility of anything affecting the calibre of the products they are producing.
Cleanroom Classifications
Cleanrooms are categorized according to the concentration and dimensions of airborne particles permitted within a given volume of air. The classification system spans from the most rigorous ISO Class 1 to the least stringent ISO Class 9. Each class is characterized by specific criteria pertaining to particle count and cleanliness standards.
Benefits of Proper Cleanroom Design and Construction
Effective cleanroom design and construction offer a myriad of advantages, such as heightened product quality and yield, bolstered safety, superior contamination control, and increased cost-effectiveness and efficiency. The establishment of a meticulously controlled environment diminishes the risk of contamination, resulting in elevated product quality and yield.
Moreover, the improved safety and contamination control measures contribute to fewer production delays and reduced downtime. The meticulous design and construction of cleanrooms also play a pivotal role in cost savings, minimizing product waste, and optimizing energy consumption.
Well, now when we know that clean rooms are VIP sections, let’s have a look what makes these sections VIP.
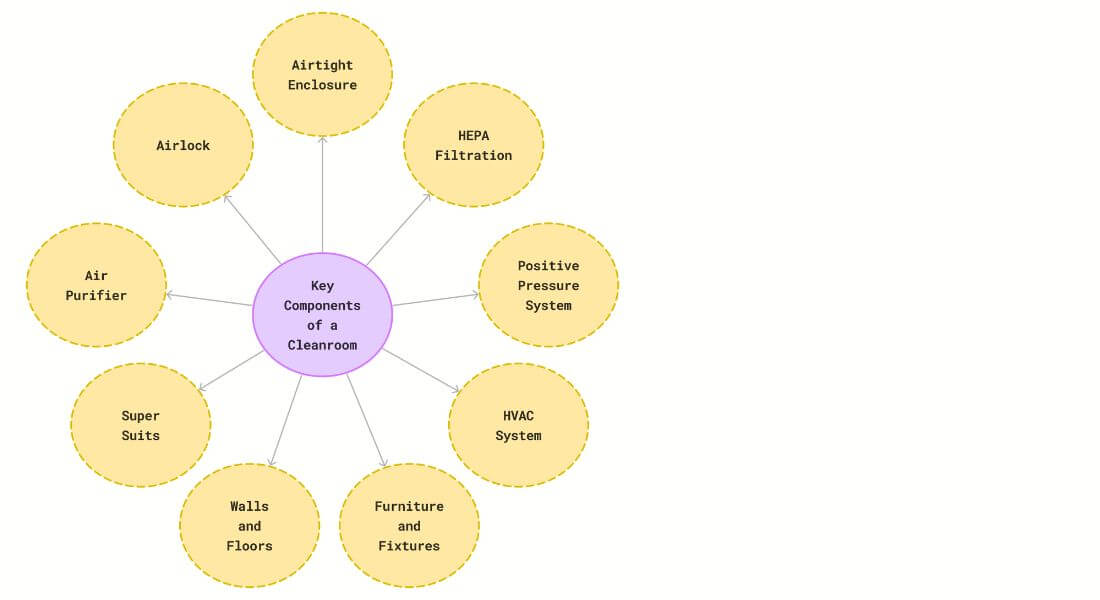
The Key Components of a Cleanroom
1. Airtight Enclosure
- Importance: A well-designed cleanroom must be an airtight enclosure. Proper sealing prevents contaminated air from infiltrating the space.
- Function: External pollutants are kept out, maintaining a sterile environment.
2. HEPA Filtration
- Role: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are essential. They efficiently capture airborne particles, maintaining the required cleanliness level.
- Application: HEPA filters protect critical areas and sensitive products.
3. Positive Pressure System
- Purpose: Cleanrooms are typically maintain positive pressure relative to the surrounding environment.
- Benefits:
i. Prevents unfiltered air from entering.
ii. Ensures that air flows from the cleanroom into adjacent areas, minimizing
iii. contamination risk.
4. HVAC Systems
- Critical Role: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are vital.
- Functions:
i. Regulate temperature and humidity.
ii. Control airflow to maintain desired conditions.
5. Cleanroom Furniture and Fixtures
- Purpose-built Items: Purpose-built furniture, workstations, and fixtures are designed for cleanroom use.
- Characteristics:
i. Easy to clean.
ii. Minimize particle generation.
iii. Contribute to overall cleanliness.
6. Cleanroom walls and floors
- The floors and walls of cleanrooms must be smooth, impervious, and free from cracks and crevices. In order to meet ISO class cleanroom standards the walls should be non-shedding.
- The floor of can be either epoxy or Heat welded vinyl. Heat welded floors are easy to clean, resistant to chemicals and are anti slippery.
- Epoxy flooring are cheaper than Heat welded vinyl and can be slippery.
7. Super suits
People working in clean room wear the advanced suits to reduce particle shedding. It feels like they’re getting ready for a space trip, only instead of heading into space, they’re developing life-saving medications or medical device.
8. Air purifiers:
Prior to entering these hygienic rooms, there’s an air shower that resembles a wind tunnel from the future. As you stand inside, filtered air is blasted over you to ensure that you are as particle-free as possible before going inside.
9. Airlocks:
The integrity of the clean room is maintained through Airlocks. Air locks are specialized chambers that act as transitional zones, serving as a buffer between different cleanliness zones. By employing controlled entry and exit procedures, airlocks prevent contaminants from infiltrating the cleanroom, ensuring a consistently controlled and purified atmosphere.
Clean Room Process
The clean room process in medical device manufacturing is designed to maintain an environment with minimal levels of contaminants such as dust, airborne microbes, aerosol particles, and chemical vapors. Clean rooms are classified according to ISO 14644-1 standards based on the concentration of airborne particles. Depending on the product’s sterility requirements, manufacturers use clean rooms ranging from ISO Class 5 (highest cleanliness) to ISO Class 8. These environments use HEPA or ULPA filters, positive air pressure, and controlled temperature and humidity to prevent contamination. Air change rates are maintained to ensure particle control, and all personnel must wear specialized gowns and follow strict entry procedures.
Materials and equipment entering the clean room must be cleaned or sterilized, and are often introduced through controlled pass-through systems. Regular cleaning using validated disinfectants is essential, along with routine environmental monitoring, including particle counts and microbial sampling. This process ensures that medical devices are manufactured under safe, hygienic, and regulatory-compliant conditions.
Why do you Require a Clean Room for Manufacturing Medical Devices?
A clean room is essential for manufacturing medical devices to ensure a controlled environment with minimal levels of contaminants such as dust, microbes, and airborne particles. Many medical devices, especially implantable or sterile products, require high levels of cleanliness to prevent contamination that could compromise patient safety. Clean rooms maintain specific temperature, humidity, and air filtration standards, significantly reducing the risk of particulate and microbial contamination. This controlled environment helps ensure product quality, regulatory compliance (e.g., ISO 13485, FDA), and patient safety. Using clean rooms also supports consistent manufacturing processes, reducing variability and defects in critical medical device components.
Operating a Clean Room
Operating a clean room involves strict adherence to protocols that control contamination, maintain cleanliness, and ensure product integrity. Key practices include controlled access, gowning procedures, and regular cleaning using approved disinfectants. Air quality is maintained through HEPA filtration and positive pressure to prevent particle ingress. Environmental parameters like temperature, humidity, and particle counts are continuously monitored. Personnel are trained in clean room behavior to minimize contamination risks. Equipment and materials entering the clean room are disinfected or sterilized. Regular validation and maintenance of systems, along with documentation, ensure compliance with standards like ISO 14644 and regulatory requirements for medical device manufacturing.
Clean Room Classification – ISO Class
Clean room classification according to ISO 14644-1 defines cleanliness levels based on the concentration of airborne particles. ISO Classes range from ISO Class 1 (most stringent) to ISO Class 9 (least stringent). For medical device manufacturing, ISO Class 7 or 8 is commonly used, depending on the product’s sterility and risk level. Each class specifies the maximum allowable number of particles per cubic meter for different particle sizes (e.g., ≥0.5 μm). Class selection depends on product requirements, regulatory standards, and manufacturing processes. Proper classification ensures controlled environments for critical processes, maintaining product safety, quality, and compliance with global regulations.
In other words, clean rooms are the superheroes of precision production, guaranteeing that all of the products they make are of the highest calibre and are free of intruders. It’s kind of cool, huh? Do you have any other questions concerning clean rooms?
Also Explore
Internal Quality Audit