Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of the healthcare sector, new medical devices often raise concerns, particularly regarding cybersecurity threats. With the advent of interconnected medical devices and AI-driven services, there’s a heightened risk of hacking and data breaches. The European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) plays a pivotal role in addressing these concerns by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of medical devices. As the healthcare industry continues its digital transformation, safeguarding sensitive data and protecting against cyber-attacks remain paramount priorities.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity encompasses the deployment of technologies, procedures, and measures to shield systems, networks, software, devices, and information from cyber threats. Its core objective is to reduce the likelihood of cyber-attacks and thwart unauthorized access to systems, networks, and technologies.
ISO 81001-1 defines cybersecurity as the state where information and systems are safeguarded against unauthorized activities, including access, use, disclosure, disruption, alteration, or destruction. This protection is vital for maintaining acceptable levels of risk to confidentiality, integrity, and availability throughout the entire life cycle of the system.
Cybersecurity involves the protection of information and systems from unauthorized access or harm. This entails safeguarding data from unauthorized viewing or modification, ensuring uninterrupted availability of systems, and preventing any disruptions or damage. Measures such as employing strong passwords, installing antivirus software, and encrypting sensitive files are effective strategies to enhance cybersecurity and safeguard personal information.
Basic Cybersecurity Concepts
It Security, Information Security, Operation Security
Annex I of the Medical Devices Regulations mandates that manufacturers of both in vitro diagnostic medical devices and medical devices adhere to specific minimum standards for hardware, IT network specifications, and IT security protocols. These standards encompass protection against unauthorized access, a crucial aspect for ensuring the proper functioning of the software as intended.
(Refer to sections 17.4, 18.8, and 23.4b in the MDR, as well as sections 16.4 and 20.4.1(c) in the IVDR)
- IT Security: According to ENISA, the Communication Security Domain pertains to safeguarding against threats targeting the technical infrastructure of a cyber system. These threats may lead to alterations in the system’s characteristics, potentially enabling activities that are not authorized by its owners, designers, or users.
- Operation Security: ENISA defines the Operation Security Domain as the protection against deliberate disruptions to processes or workflows, which could result in outcomes not intended by the system’s owners, designers, or users.
- Information Security: As per ENISA’s definition, the Information Security Domain pertains to guarding against the risk of theft, deletion, or modification of stored or transmitted data within a cyber system.
Additional definitions encompass broader concepts such as Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA). These principles emphasize maintaining the confidentiality of data, ensuring its integrity, and guaranteeing its availability when needed.
Information Security
Information security is characterized as the protection of data or information systems from unauthorized access, destruction, or disruption. Security professionals commonly refer to three fundamental concepts:
- Confidentiality – Ensuring that only authorized users can access the information.
- Integrity – Guaranteeing that information cannot be altered without authorization, and that any modifications are detected while maintaining consistency.
- Availability – Ensuring that information is readily available and that communication channels function properly when required.
Cybersecurity Requirements In EU MDR 2017/745
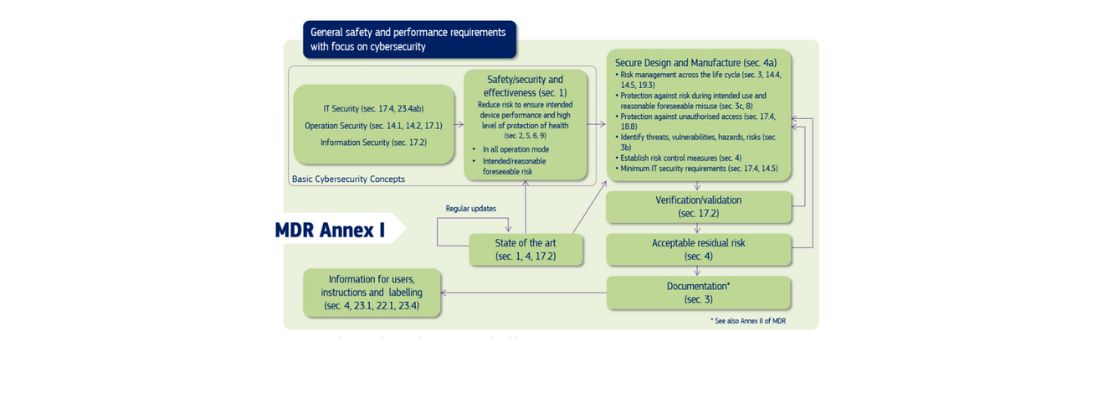
The cybersecurity regulations within the Medical Devices Regulations encompass both pre-market and post-market phases, as detailed in Chapter 2 of the regulations to aid manufacturers in compliance. This guidance is utilized to formulate recommendations and instructions for manufacturers in subsequent chapters (3-6) of the document MDCG 2019-16 Guidance on Cybersecurity for medical devices.
Figure 1: Cybersecurity requirements contained in MDR Annex I
The regulations depicted in Figure 1 for medical devices are equally applicable to in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDs). To facilitate manufacturers in meeting the requirements for both device types, we’ve prepared a table (Table 1) that correlates the sections in the regulations for medical devices (MDR Annex I) with the corresponding sections for IVDs (IVDR Annex I). This table serves as a guide for ensuring compliance across both device categories.
Other Cybersecurity Requirements Which Are Not In Mdr 2017/745
Certain cybersecurity requirements, such as safeguarding privacy and maintaining data confidentiality, may not be explicitly outlined in the Medical Devices Regulations. Instead, these rules might be governed by other legislation specifically addressing data protection and privacy concerns.
Concerning cybersecurity within the Medical Devices Regulations, manufacturers should pay particular attention to the following provisions:
- Privacy and data protection: Article 62.4(h) outlines general requirements concerning clinical investigations conducted to demonstrate device conformity.
- Conformity assessment procedures are detailed in Article 52.
- Manufacturers must adhere to provisions regarding the post-market surveillance system (Article 83), post-market surveillance plan (Article 84), post-market surveillance report (Article 85), and periodic safety update report (Article 86).
- Technical documentation requirements are specified in Annex II, including technical documentation on post-market surveillance outlined in Annex III.
- Clinical evaluation and post-market follow-up requirements are elaborated in MDR Chapter VI and Annex XIV.
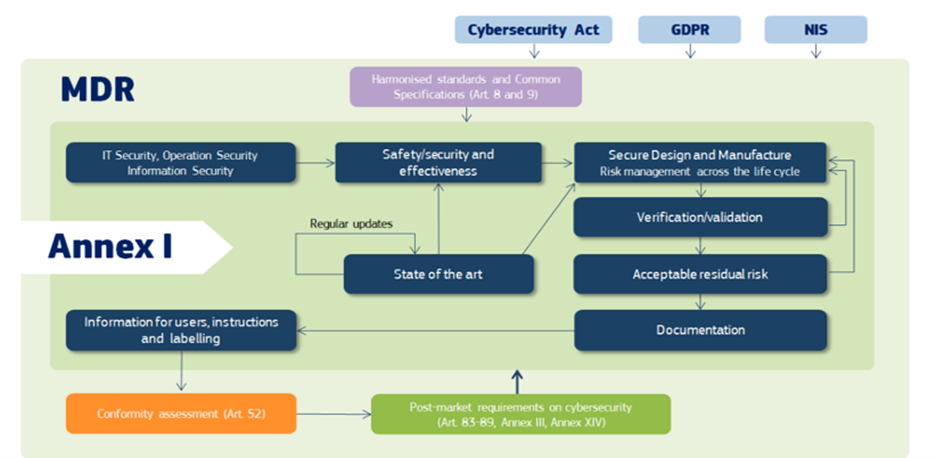
Figure 2: Cybersecurity requirements in the MDR; the application of other relevant EU legislations, such as Cybersecurity Act, GDPR and NIS
According to the Medical Devices Regulations, manufacturers are obligated to employ the most current technology and knowledge during the design, development, and updating phases of medical devices. They must demonstrate that they are leveraging the best available information to mitigate security risks effectively.
What is GDPR?
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is an extensive data protection legislation applicable throughout Europe, supplanting the EU’s Data Protection Directive from 1995 and associated member state laws since May 25, 2018. This modern law grants individuals greater authority over the usage of their personal information. Moreover, it holds organizations accountable for safeguarding this data and mandates strict regulations regarding its collection and processing.
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) mandates that organizations must institute suitable security measures to safeguard personal data. Failure to do so could result in significant fines.