What is the CE Mark Logo?
The CE Mark logo is a critical symbol for manufacturers and distributors who want to place their products in the European Economic Area (EEA). It acts as a declaration by the manufacturer that the product meets the essential requirements set by EU regulations related to health, safety, and environmental protection.
For industries like medical devices and in vitro diagnostic (IVD) products, CE marking is not optional — it’s a legal requirement under the EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation 2017/745) and IVDR (In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation 2017/746). Affixing the CE mark confirms that the product has successfully undergone the necessary conformity assessment procedures and can be marketed across Europe without additional national approvals.
Key Performance Requirements for CE Marking
Before a medical device or IVD can bear the CE logo, manufacturers must demonstrate compliance in three critical areas:
- Scientific Validity: Scientific validity ensures that the product achieves its intended purpose based on established scientific principles. For IVDs, this involves confirming the relationship between the analyte and the clinical condition or physiological state.
- Analytical Performance: This measures the accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and specificity of the device. Analytical performance validation is essential for laboratory instruments, diagnostics, and monitoring devices.
- Clinical Performance: The product must demonstrate that it delivers the intended clinical benefit when used as directed. For high-risk medical devices, this usually involves clinical investigations or real-world evidence under EU MDR/IVDR.
These performance evaluations form the foundation of the technical documentation required for CE marking.
Affixing the CE Logo: What It Signifies
Once the CE logo is affixed to a product, it communicates that the product is:
- Fully compliant with EU regulations
- Safe and effective for the intended use
- Ready for free circulation within the EEA market
For importers and exporters, especially those selling products manufactured outside the EU, affixing the CE mark is essential. Without it, the product cannot be legally placed on the European market.
Where Should the CE Mark Be Placed?
The CE logo must be:
- Visible to the user and authorities
- Legible and easily identifiable
- Indelibly affixed to ensure it cannot be removed or tampered with
Acceptable Locations:
- Directly on the product (preferred)
- On the data plate or nameplate
- On the outer packaging
- In accompanying documents like user manuals or instructions for use (IFU)
If direct marking on the device isn’t technically possible or appropriate due to size or material limitations, alternate placements are allowed—but they must still comply with Article 20 of MDR/IVDR.
Design Standards for the CE Logo
The CE mark has strict design specifications. Modifying or misrepresenting the logo is not permitted.
Important Design Guidelines:
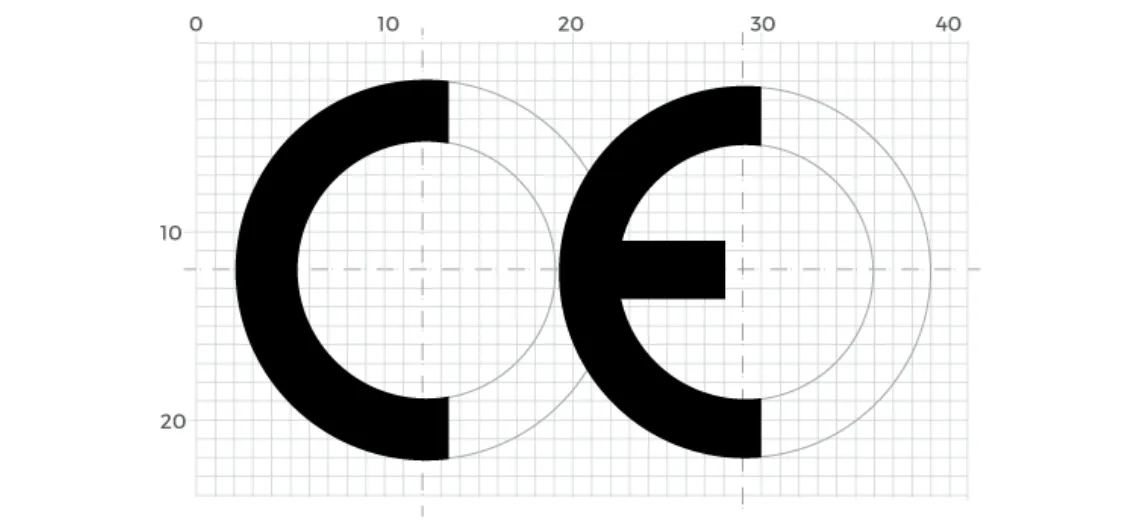
- The letters ‘C’ and ‘E’ must be formed using specific geometric proportions based on imperfect semi-circles.
- The arms of the C are extended longer than a standard semicircle by one square unit.
- The space between the C and E is also precisely defined to maintain clarity and recognition.
Minimum Size Requirement:
- The CE logo must be at least 5 mm in height
- It can be scaled up, but the proportions must not be distorted
- It must never be stylized, combined with other symbols, or partially obscured
These design rules are outlined in the EU Blue Guide, which provides best practices for placing products on the EU market.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using a fake or altered CE logo (including the notorious “China Export” mark)
- Affixing the CE mark before completing conformity assessment
- Skipping technical documentation or Declaration of Conformity (DoC)
- Not consulting a Notified Body for Class II or Class III devices
- Failing to register in EUDAMED, the European database for device registration
Why the CE Logo Matters for Medical Device Companies
For medical device companies, CE marking is not just a legal requirement – it provides strategic advantages:
- Market Access to all EU/EEA countries
- Competitive Edge by demonstrating regulatory compliance
- Reduced Trade Barriers through harmonized standards
- Improved Credibility with regulators, partners, and users
By meeting CE marking standards, companies align with the Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF) principles and make future entry into other regulated markets easier (e.g., UKCA, FDA, TGA).
Conclusion
The CE mark logo is much more than a visual stamp. For medical device and IVD companies, it’s a critical indicator that the product complies with EU regulatory expectations, can be trusted by healthcare professionals, and is ready for the European market.
Whether you’re a startup launching your first diagnostic product or an established manufacturer updating your device to align with IVDR/MDR, getting the CE logo right is a vital step in your compliance journey.
Need Help with CE Marking?
At Maven Profcon Services LLP, we specialize in guiding manufacturers through every step of the CE marking process—from risk classification and technical documentation to performance evaluation and regulatory strategy.